Meta-description:
A sharp, evidence-based review explaining the real role of Vitamin D in orthopedics — osteoporosis, fracture prevention, and fracture healing. Learn what Vitamin D actually does, what it absolutely does not do, and how to supplement it correctly based on high-quality evidence.
Vitamin D and Osteoporosis — Enabler, Not Builder
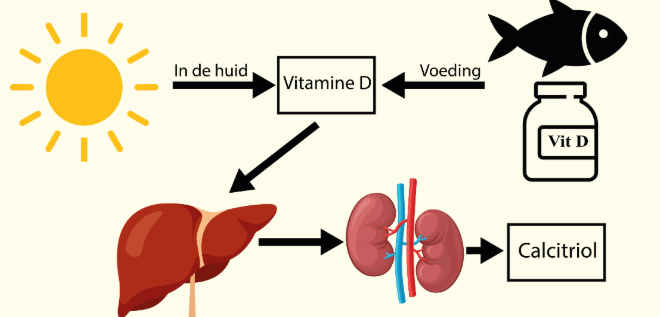
When discussing Vitamin D and osteoporosis, the first misconception must be destroyed: Vitamin D is not an anabolic bone-forming drug. It is an enabling hormone. Its primary mission is to maintain calcium-phosphate homeostasis, ensuring intestinal absorption of calcium so bones can mineralize. Without Vitamin D, giving calcium is like delivering cement without water.
Multiple meta-analyses, including studies published in The Lancet, show that Vitamin D alone does not significantly increase bone mineral density (BMD) in healthy adults. However, Vitamin D + calcium together result in measurable improvements in elderly patients — a statistically significant but modest increase in BMD.
The clinical message is uncomfortable but unavoidable:
Supplementing Vitamin D without adequate calcium intake is biologically pointless.
Vitamin D’s true orthopedic value lies in functioning as the foundation that allows osteoporosis medications (e.g., bisphosphonates, denosumab) to work safely and effectively, preventing hypocalcemia during therapy.
Vitamin D and Fracture Risk — Prevention Only If Combined
Few areas in orthopedics have seen such dramatic scientific reversals as Vitamin D for fracture prevention. Large-scale RCTs and systematic reviews (Cochrane, JAMA, VITAL) now provide an unequivocal conclusion:
- Vitamin D alone does NOT reduce hip, vertebral, or total fracture risk.
- Vitamin D + calcium DOES reduce fracture risk — especially hip fractures, with a relative reduction of approximately 16%.
However, this benefit is population-specific, not universal. The clearest effect is found in:
- Frail elderly patients
- Nursing-home residents
- Individuals with low sunlight exposure and malnutrition
These patients aren’t receiving “supplementation” — they’re receiving deficiency correction, which is therapeutically different.
And here is the biggest clinical trap:
🚫 Avoid high-dose bolus therapy (e.g., 300,000–500,000 IU yearly injections).
RCTs show it paradoxically increases falls and fractures.
The evidence-supported sweet spot for fracture prevention:
➡ 800–1,000 IU/day of Vitamin D + adequate dietary calcium
Vitamin D and Fracture Healing — Necessary but Not Accelerating
This is the battlefield orthopedic surgeons care about most: Does Vitamin D speed fracture healing?
Mechanistically, the argument is flawless. Vitamin D:
- Maintains calcium delivery for callus mineralization
- Influences mesenchymal stem cell → osteoblast differentiation
- Modulates VEGF and angiogenesis
Clinically, Vitamin D deficiency is extremely common after fractures (up to 70–85%), and deficiency is a well-established risk factor for delayed union and nonunion.
However — and this is the unkind twist —
RCTs show Vitamin D supplementation does not accelerate fracture healing in patients who already have normal Vitamin D levels.
Vitamin D plays a permissive role, not a pro-healing role:
- Correcting deficiency prevents impaired healing
- Supplementing a normal patient does not make bone heal faster
In other words, Vitamin D doesn’t step on the gas — it removes the brake.
Practical, Evidence-Aligned Clinical Strategy
If we cut through the noise and follow the best available data, the orthopedic protocol becomes crystal-clear:
🔹 For fracture prevention
- General population: Vitamin D alone — not recommended
- Frail / institutionalized elderly: Vitamin D + calcium — recommended
- Target daily dose: 800–1,000 IU
- Never use annual megadose bolus therapy
🔹 For osteoporosis management
- Vitamin D + calcium is the non-negotiable foundation
- It enables osteoporosis medications to work safely and effectively
🔹 For fracture treatment
- Test 25(OH)D levels
- If <20–30 ng/mL → correct deficiency immediately
- Goal is normal healing potential, not “super-healing”
A useful and constantly updated reference on Vitamin D physiology and clinical ranges:
🔗 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560636/
Bottom Line — The Rules That Never Fail
| Clinical Scenario | Best Evidence-Based Action |
|---|---|
| Prevent fractures in general population | ❌ Vitamin D alone |
| Prevent fractures in frail elderly | ✅ Vitamin D + calcium |
| Treat osteoporosis | 🔑 “Foundation therapy” for all anti-osteoporotic drugs |
| Support fracture healing | ⚠ Correct deficiency; don’t expect acceleration |
| Preferred dosing | 800–1,000 IU/day |
| Avoid | 💣 High-dose bolus therapy |
Vitamin D is not the miracle many assumed. But it is not useless either.
Its power lies in precision, not exaggeration.
Not everyone needs it.
But for the right patients, in the right dose, paired with calcium, it absolutely prevents harm and improves orthopedic outcomes.
Disclaimer:
This article and all articles on this website are for reference only by medical professionals; specific medical problems should be treated promptly. To ensure “originality” and improve delivery efficiency, some articles on this website are AI-generated and machine-translated, which may be inappropriate or even wrong. Please refer to the original English text or leave a message if necessary. Copyright belongs to the original author. If your rights are violated, please contact the backstage to delete them. If you have any questions, please leave a message through the backstage, or leave a message below this article. Thank you!
Like and share, your hands will be left with the fragrance!
More info. https://linktr.ee/shifreeman