Patellar fractures, particularly transverse ones, can severely impair the knee’s extensor mechanism if not addressed promptly. The Kirschner wire tension band technique is a tried-and-true surgical method for restoring joint function, ensuring anatomical reduction, and promoting early mobilization. This article provides a detailed breakdown of the procedure, from preparation to postoperative care, highlighting its effectiveness and key considerations.
Step-by-Step Guide to the Kirschner Wire Tension Band Technique
1. Preoperative Setup
Proper preparation is critical for a successful outcome.
- Patient Positioning: Place the patient supine on a radiolucent operating table, ensuring easy access to the knee.
- Anesthesia: Administer either general or regional anesthesia based on patient needs.
- Sterilization: Prepare the surgical site with an antiseptic solution and drape the area to maintain sterility.

2. Surgical Exposure
- Incision: Make a midline longitudinal incision over the patella, providing direct access to the fracture site.
- Soft Tissue Handling: Carefully expose the patella while preserving nearby soft tissues, including the retinaculum, to minimize postoperative complications.
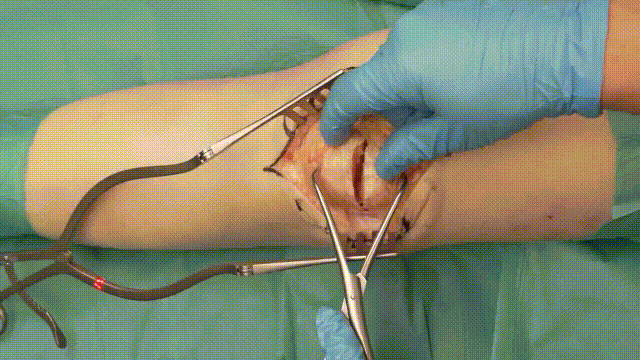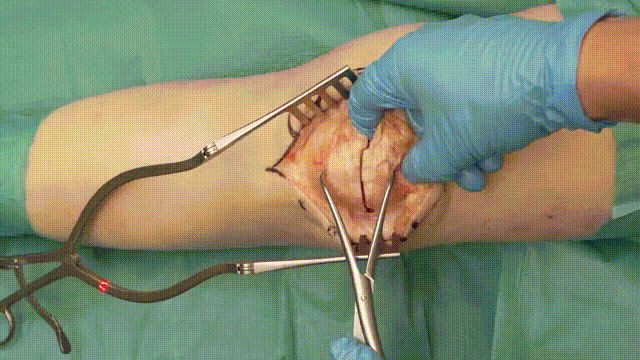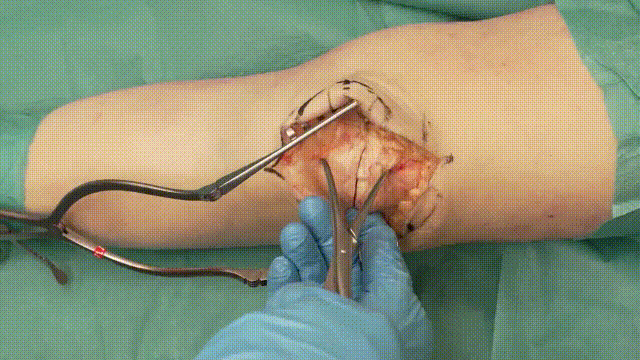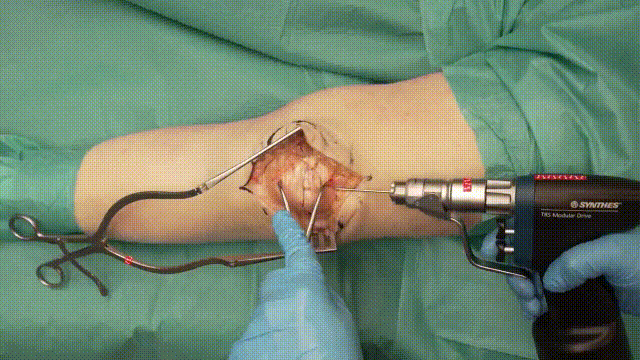
3. Fracture Reduction
- Debridement: Remove hematomas, debris, or interposed soft tissue to ensure a clean fracture site.
- Reduction: Achieve anatomical alignment by manually reducing the fracture fragments. Temporary fixation with clamps or small K-wires may assist in maintaining alignment.
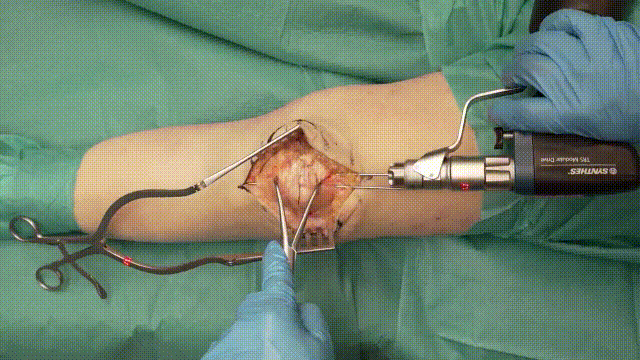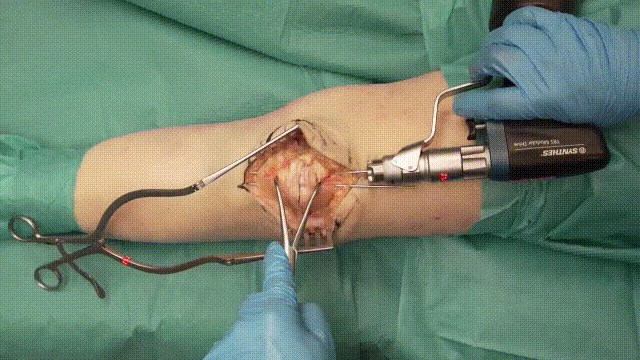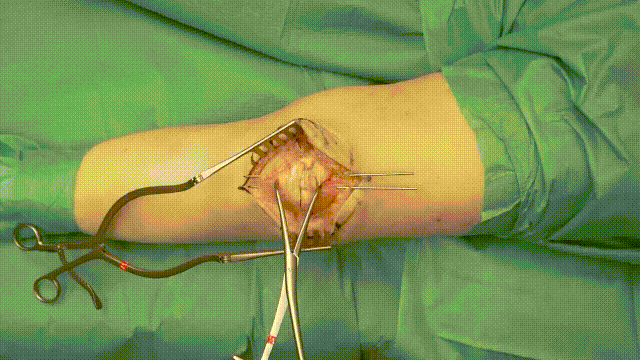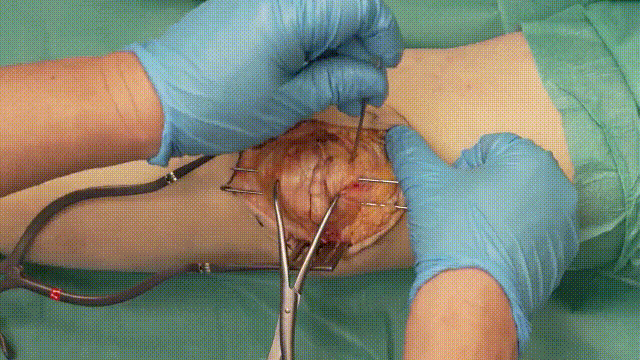
4. Kirschner Wire Placement
- Insertion: Insert two parallel K-wires (1.6–2.0 mm) longitudinally across the fracture. Position the wires about 5 mm from the anterior cortical surface of the patella.
- Positioning: Ensure the wires securely penetrate the distal and proximal poles without excessive protrusion, reducing risks of irritation.
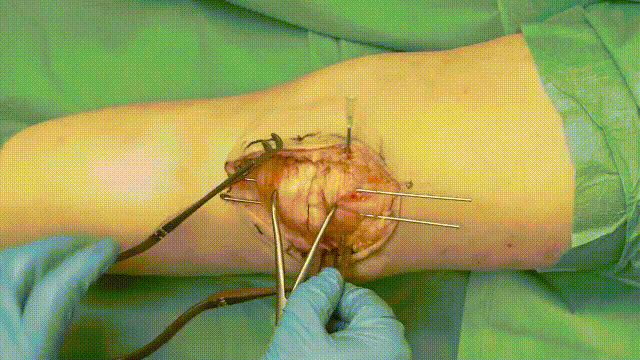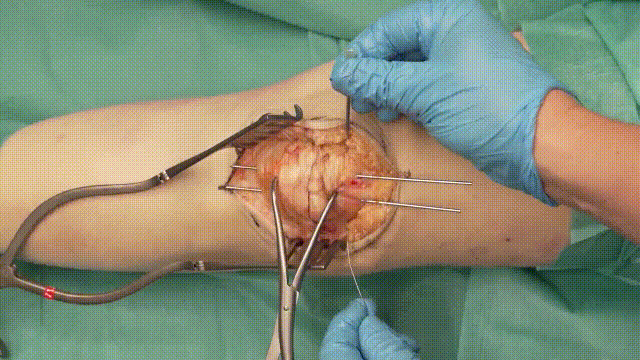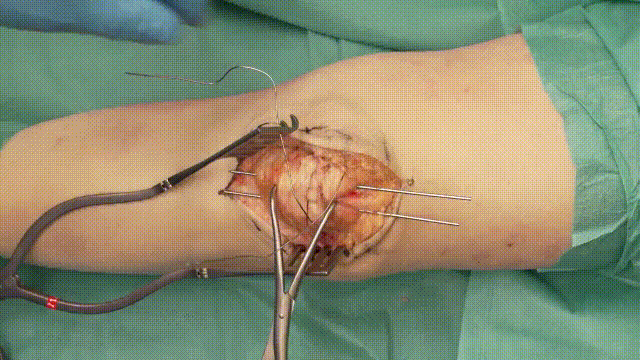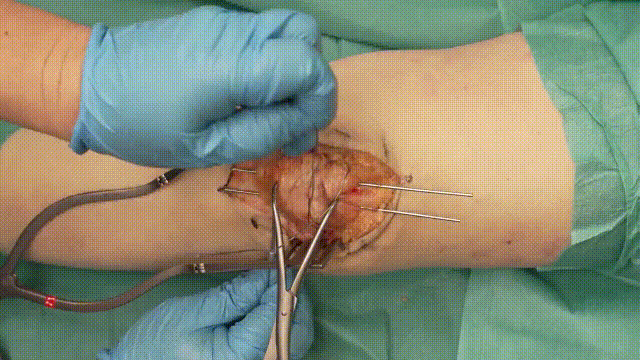
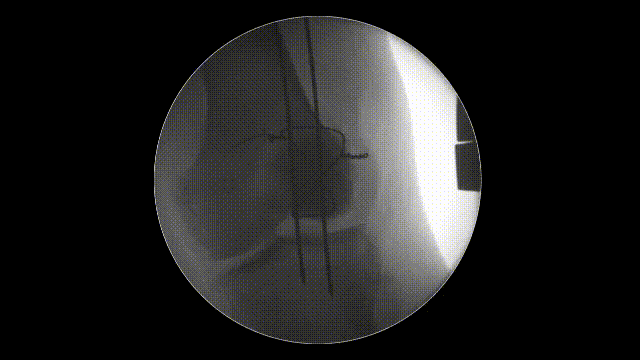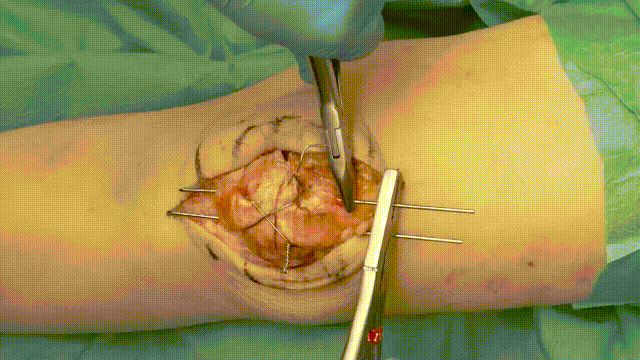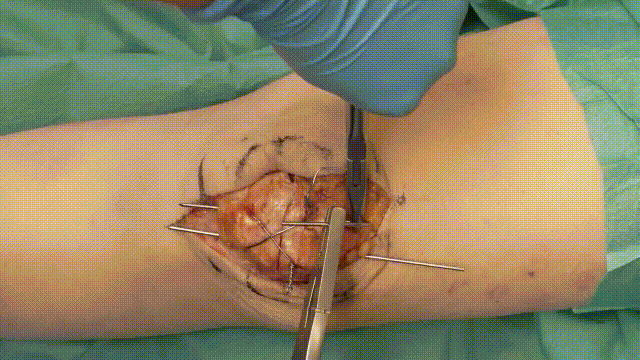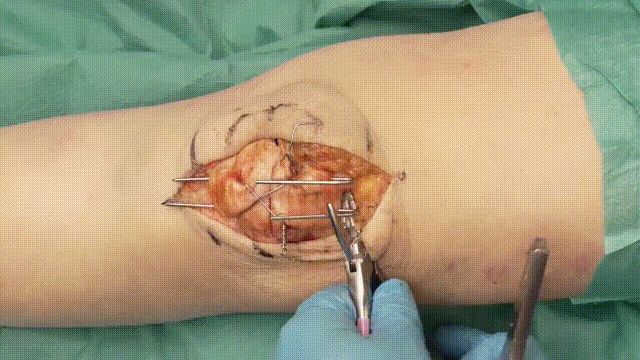
5. Application of the Tension Band
- Wire Looping: Pass an 18-gauge stainless steel cerclage wire in a figure-of-eight configuration around the K-wires. The wire should loop anteriorly over the patella and posteriorly through the quadriceps and patellar tendons.
- Tensioning: Tighten the cerclage wire evenly to compress the fracture fragments, converting tensile forces into compressive forces at the fracture site.
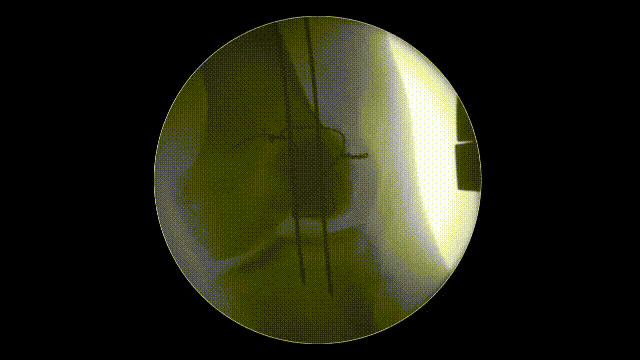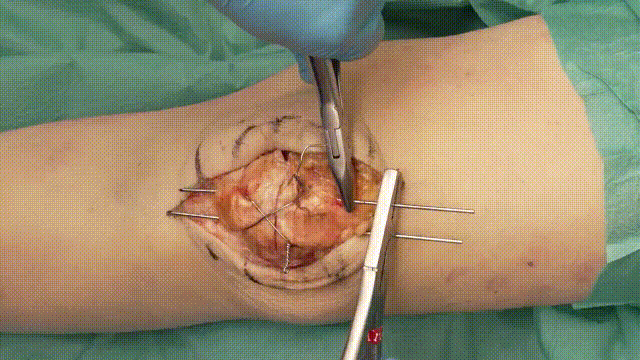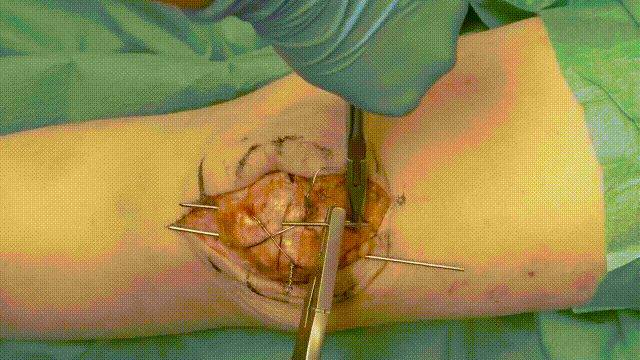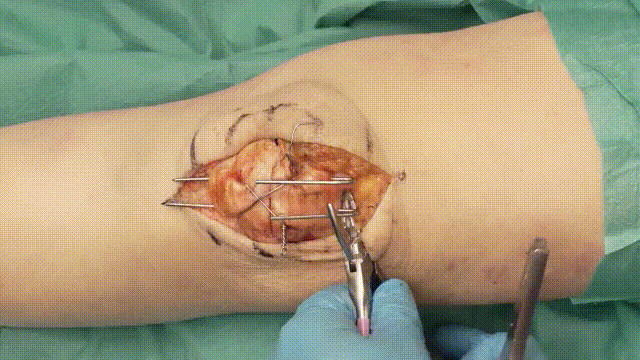
6. Verification of Fixation
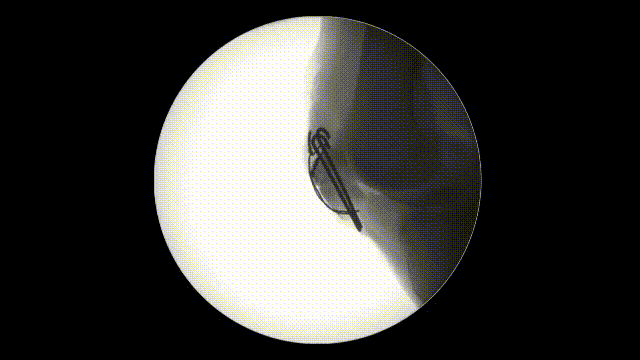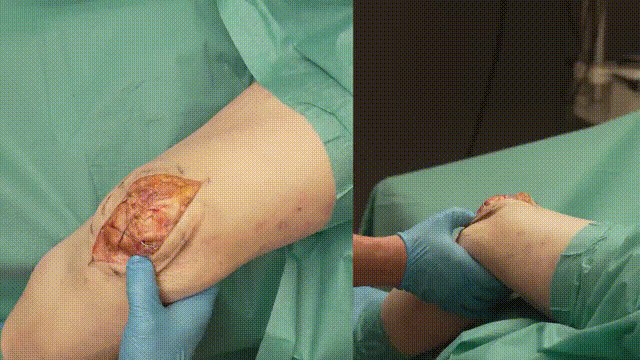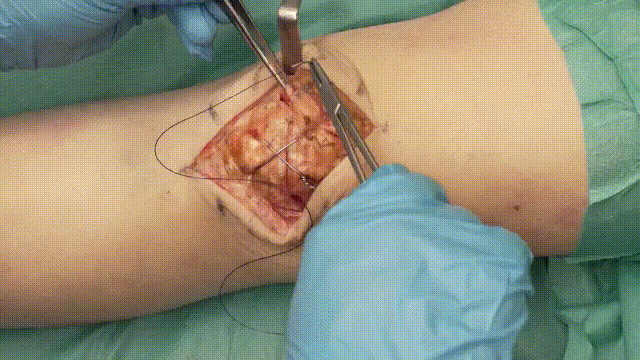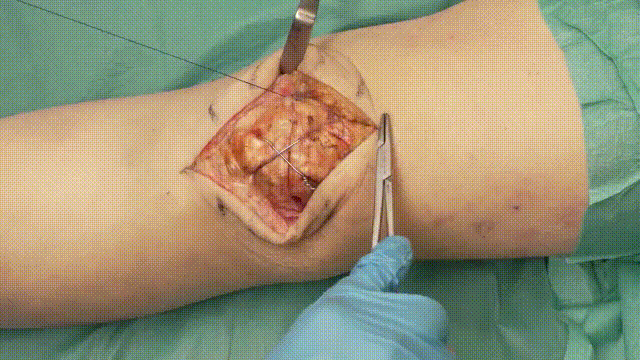
- Stability Check: Flex and extend the knee intraoperatively to confirm that the fixation is stable and the fracture remains reduced.
- Imaging: Use intraoperative fluoroscopy to verify proper alignment, K-wire placement, and optimal tension in the cerclage wire. Learn more about fluoroscopic imaging here.
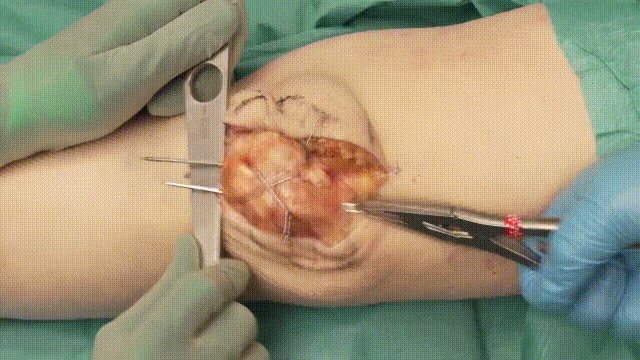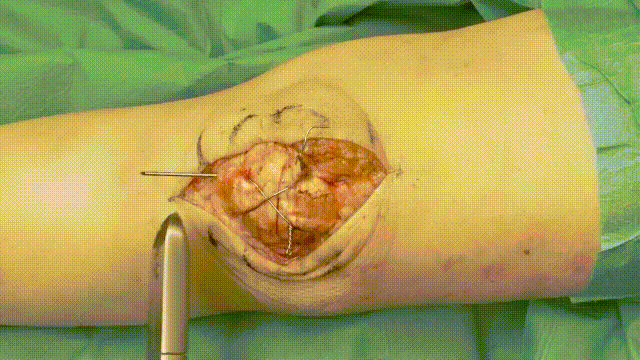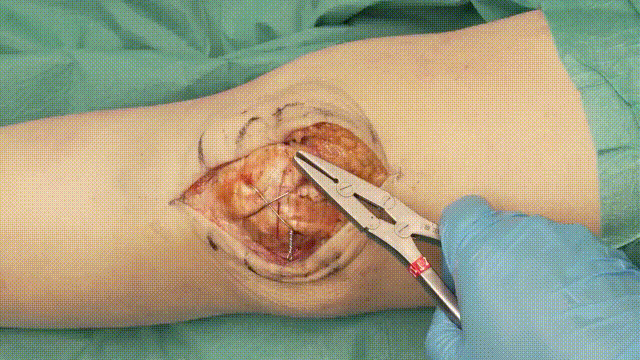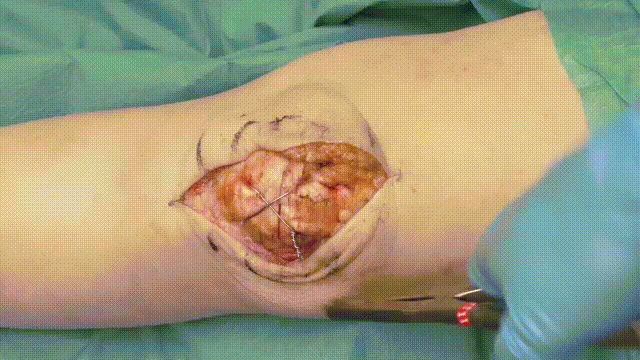
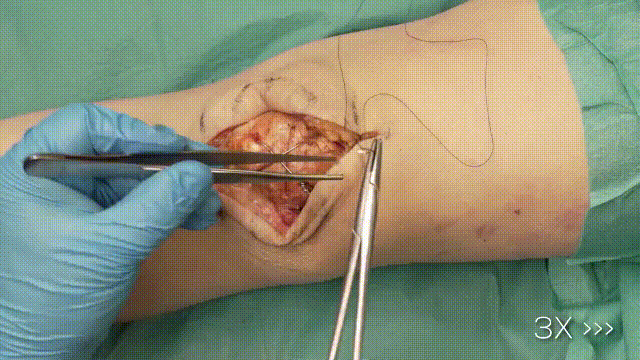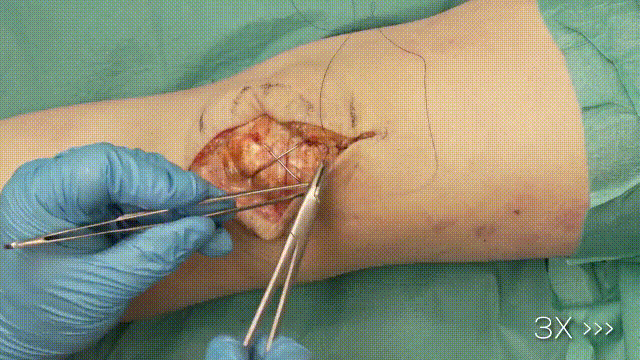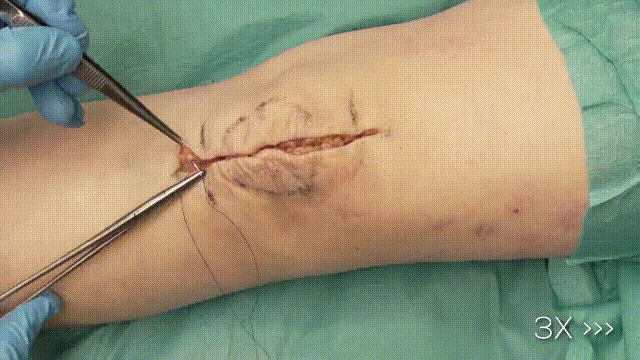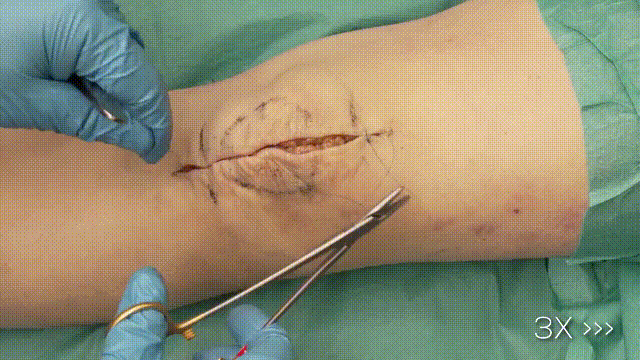
7. Final Steps
- Trimming Wires: Cut and bend the K-wire ends, ensuring they are buried beneath the soft tissue to minimize irritation.
- Closure: Close the retinaculum and soft tissues in layers, using absorbable sutures for deeper layers and non-absorbable sutures for the skin.
- Dressing: Apply a sterile dressing and immobilize the knee in full extension with a brace or splint.
Postoperative Care and Rehabilitation
- Early Mobilization: Begin range-of-motion exercises within 1–2 weeks, depending on the stability of the fixation.
- Follow-Up: Perform regular radiographic evaluations to monitor fracture healing and hardware position.
Key Considerations for Optimal Results
- Complications: While effective, this method may have complications, including wire migration, skin irritation, or the need for hardware removal in 30–52% of cases.
- Alternatives: For specific fracture patterns, consider alternative techniques like suture materials or anti-rotation strategies to reduce complications.
- Gold Standard: Despite potential issues, the Kirschner wire tension band technique remains the gold standard for patellar fracture fixation due to its simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and reliable outcomes.
Meta Description
Learn the step-by-step process of the Kirschner wire tension band technique for patellar fracture fixation. Discover its benefits, potential complications, and why it’s the gold standard for restoring knee function.
Disclaimer:
This article and all articles on this website are for reference only by medical professionals; specific medical problems should be treated promptly. To ensure “originality” and improve delivery efficiency, some articles on this website are AI-generated and machine-translated, which may be inappropriate or even wrong. Please refer to the original English text or leave a message if necessary. Copyright belongs to the original author. If your rights are violated, please contact the backstage to delete them. If you have any questions, please leave a message through the backstage, or leave a message below this article. Thank you!
Like and share, your hands will be left with the fragrance!