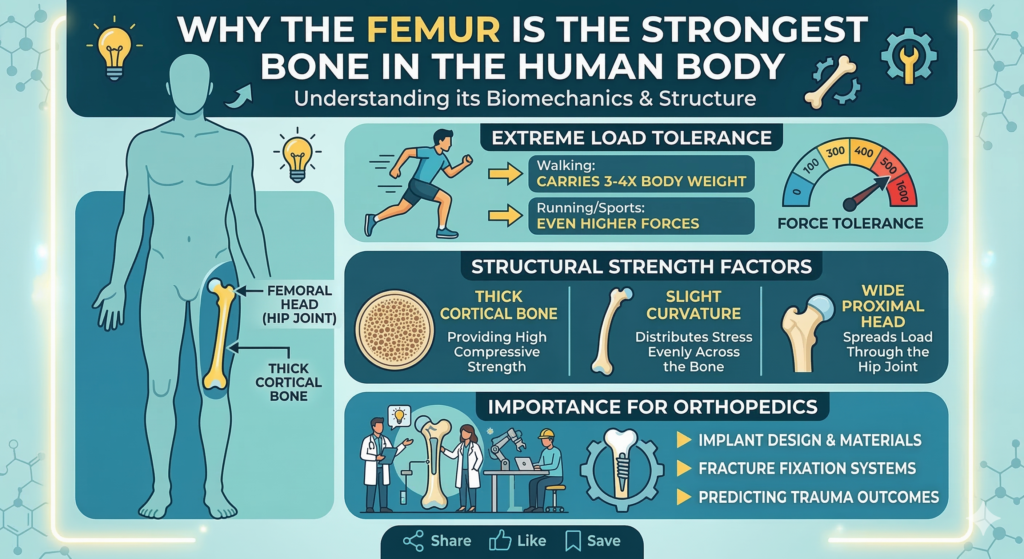
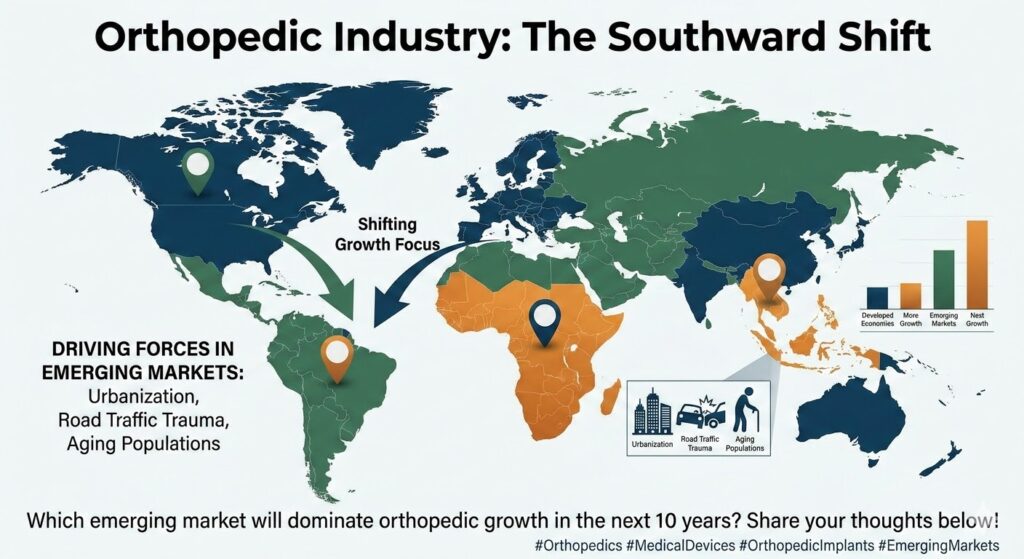
There's no limit on how long a meta description can be, but the snippet is truncated in Google Search results as needed, typically to fit the device width.
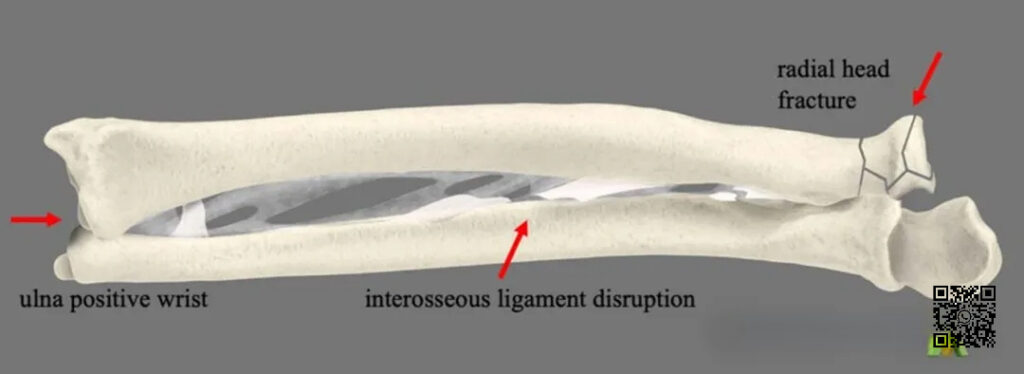
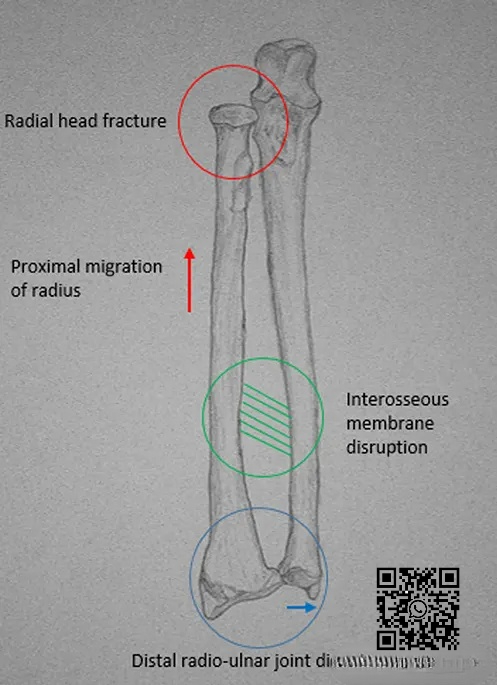
▲ Diagram showing the pattern of Essex-Lopresti injury.
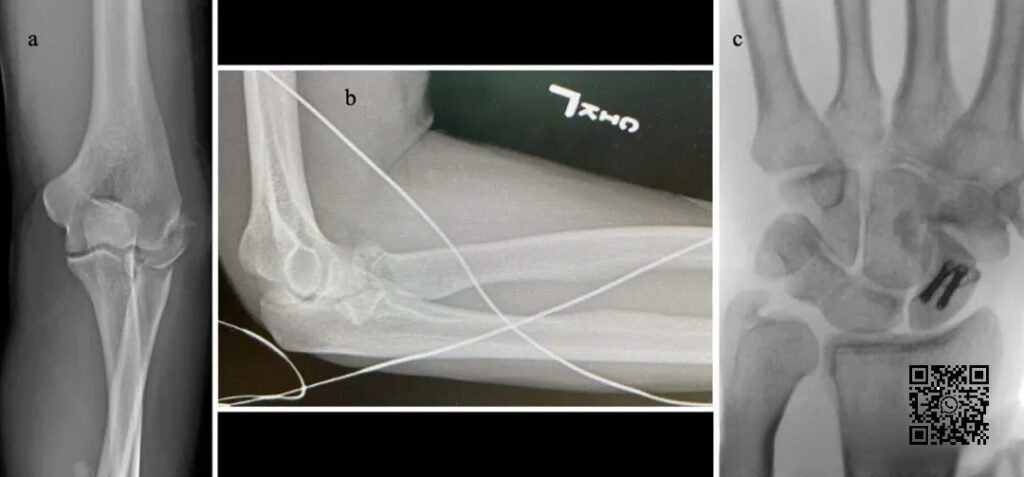
▲ The figure shows a typical case of Essex-Lopresti injury. It can be seen that the radial head is comminuted, the proximal radius of the distal radioulnar joint is displaced, and the ulnar styloid process shows positive variation.
Essex-Lopresti injury is relatively rare in clinical practice. In clinical work, some scholars have found a type of injury with the opposite injury mechanism and clinical manifestations to Essex-Lopresti injury, which is called “reverse Essex-Lopresti injury”. It should be paid attention to in clinical practice to avoid missed diagnosis.
In the case of external rotation and valgus of the forearm, the axial violence from the hand preferentially acts on the radius, causing distal radial fracture and distal and proximal oblique cords of the interosseous membrane. At this time, the interosseous membrane of the radius and ulna is only connected by the tougher central bundle. The rotation of the radius with the attachment point of the central bundle as the fulcrum causes radial head dislocation, and the radial side of the forearm loses support, the elbow is valgus, and the medial collateral ligament injury or proximal ulna fracture is caused.
Case:
A 42-year-old woman fell down the stairs. Wrist X-ray showed radial metaphysis fracture, accompanied by proximal displacement of the radius and positive ulnar variation. Elbow X-ray showed widening of the medial gap of the humero-ulnar joint.
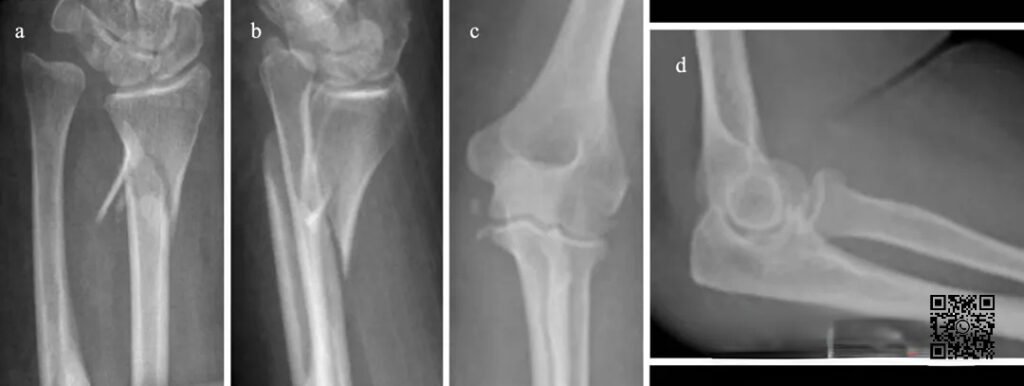
When valgus stress is applied during surgery, the medial space is significantly widened:
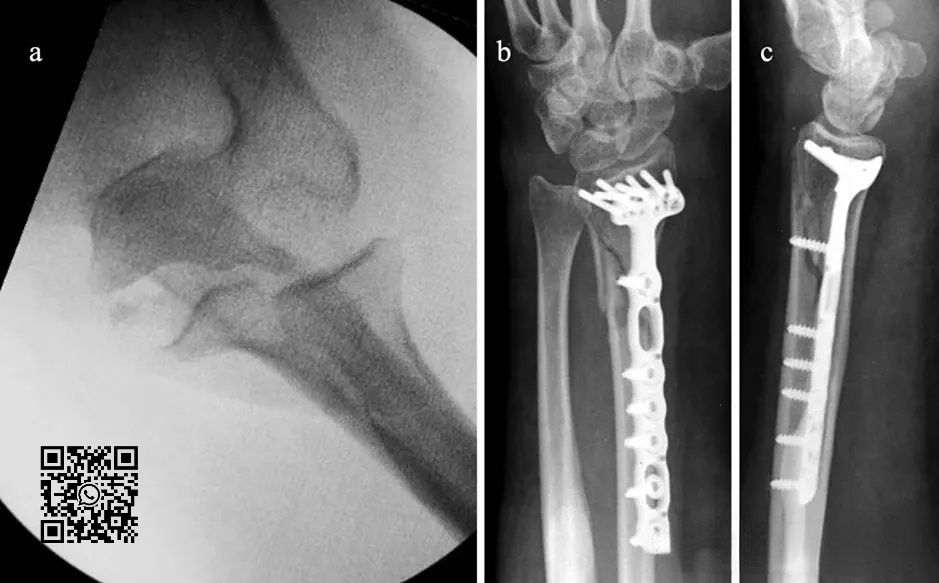
After fixation of the distal end of the radius for 1 week, the patient felt hand rotation disorder, and radiographs revealed anterior dislocation of the radial head. A second-stage operation was performed to reconstruct the proximal oblique cord of the interosseous membrane:
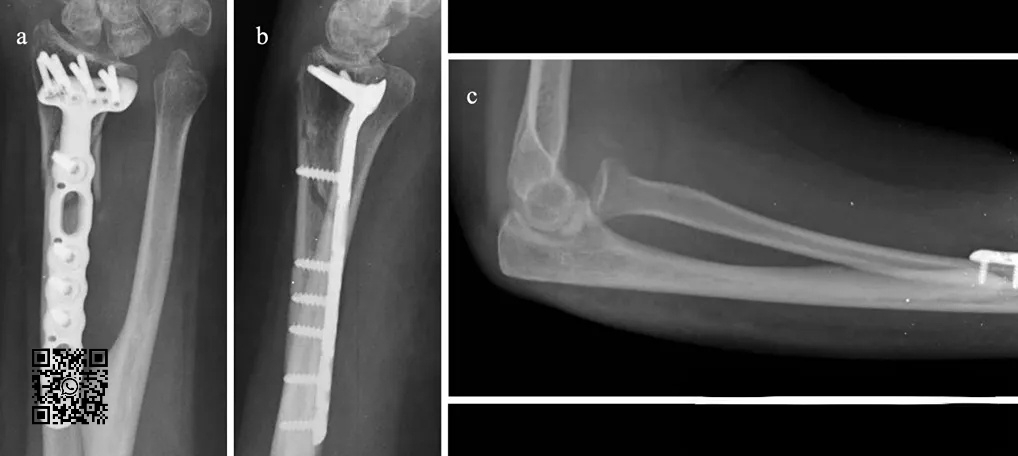
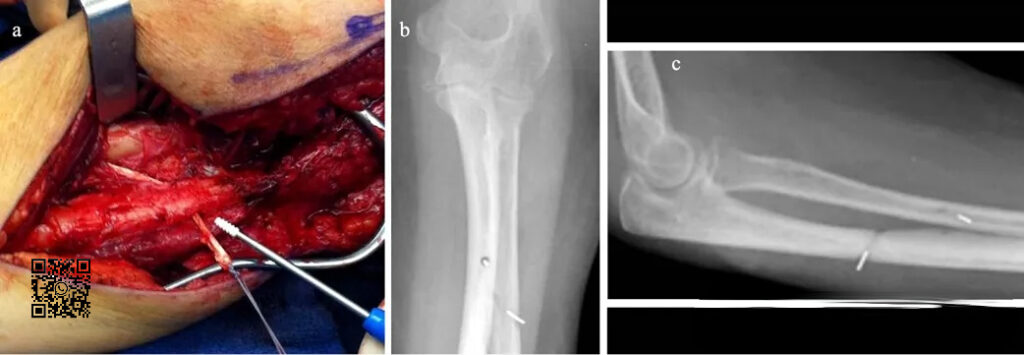
Forearm trauma is more complex and requires high reduction. The lower radioulnar joint, proximal radioulnar joint, radius, ulna and interosseous membrane form a stable structure.
Due to different injury mechanisms, there may be combined injuries of varying degrees, and clinically, “single fracture” may be the most prominent manifestation, which is easy to miss. A deep understanding of the injury mechanism and consideration of possible combined injuries are the prerequisites for effective diagnosis and treatment.
[Statement]: The concepts, technologies, and principles shared on this platform are all publicly available journals, published books, or online platform materials. The copyright belongs to the original author. The platform only organizes, summarizes, and shares them for learning reference. This platform is not responsible for the authenticity of the content and the effectiveness of the technology. The related medical behaviors generated based on the content pushed by this platform have nothing to do with the platform. Please choose carefully. If there is any infringement, please contact us to delete it.
Welcome to share, forward and like the article in the lower right corner!