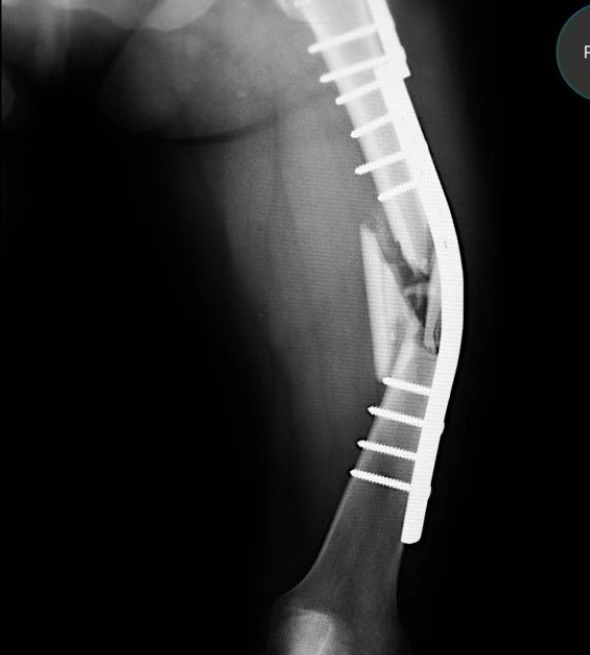
Clavicle fractures are among the most common types of fractures, accounting for 2.6% to 12% of all fractures. Of these, midshaft clavicle fractures make up a significant 80%, making it a key focus of research and treatment. Clavicle fractures not only impact bone structure but can also affect the function of the shoulder girdle, which is why effective treatment of midshaft clavicle fractures has been a hot topic in the orthopedic community.
Conservative Treatment vs. Surgical Treatment
Consensus on Conservative Treatment
Conservative treatment has traditionally been the go-to approach for midshaft clavicle fractures, usually involving symptomatic treatment and short-term immobilization. Common immobilization methods include figure-of-eight bandages and arm slings. However, recent studies suggest that figure-of-eight bandages may cause axillary nerve compression and skin issues, leading many experts to recommend simpler arm sling immobilization.
- Malunion: Conservative treatment cannot correct fracture displacement, potentially leading to 1.2 cm to 3 cm of shortening, with nonunion rates as high as 15% and symptomatic malunion rates reaching 30%.
- Functional Impact: While malunion may alter shoulder girdle function, most patients experience minimal impact on daily activities.
Controversies in Conservative Treatment
Though conservative treatment shows good short-term outcomes, mid- to long-term follow-ups reveal that some patients may develop shoulder dysfunction. A 2016 JOT study reported that malunion is closely associated with glenohumeral arthritis, particularly in athletes or patients with high physical demands, where conservative treatment may underperform compared to surgical options.
Advantages and Challenges of Surgical Treatment
Surgical treatment has gained popularity in recent years, particularly for severely displaced or comminuted fractures. Surgery significantly reduces the risk of nonunion and malunion, especially in younger patients and athletes.
Consensus on Surgical Treatment
- Surgery is simple with low complication rates and effectively improves functional recovery.
- Surgery may result in skin scarring, localized numbness, and other minor issues, but these generally do not significantly affect the patient’s quality of life.
- Athletes undergoing surgery recover faster, with a 2010 American study showing that surgically treated athletes returned to the field in 8.8 weeks, compared to 1.5 seasons for those treated conservatively.
Controversies in Surgical Treatment
- Despite its many advantages, some experts argue that there is over-surgery in cases where fractures are not severely displaced.
- The primary debate in surgical treatment revolves around the choice between plate fixation and intramedullary (IM) nailing, with both methods having their proponents.
Plate Fixation vs. Intramedullary Nailing
Pros and Cons of Intramedullary Nailing
Intramedullary nailing theoretically offers several advantages, such as less invasive surgery and faster recovery. However, its anti-displacement ability is weaker compared to plate fixation, and its long-term efficacy is less certain. Some studies, like Chuang et al., report a 100% healing rate with no significant complications, but overall, IM nailing still requires further technological improvements.
Pros and Cons of Plate Fixation
Plate fixation is considered the gold standard for complex fractures, particularly for comminuted fractures. Compared to IM nailing, plate fixation offers superior biomechanical stability, although it may cause soft tissue irritation and skin scarring.
Plate Placement: Superior vs. Anterior
When opting for plate fixation, there is a choice between placing the plate on the superior aspect or the anterior aspect of the clavicle. Both options have their advantages:
- Superior placement: Easier to attach and conform to the bone surface but may endanger the subclavian neurovascular structures.
- Anterior placement: Protects important neurovascular structures and causes less plate prominence but requires more muscle dissection.
Lim et al. found that anterior-inferior plates resulted in lower pain scores compared to superior plates, though further research is needed to confirm this finding.
Conclusion
The treatment of midshaft clavicle fractures remains a subject of debate. From conservative treatment to surgical intervention, doctors and patients must choose the most appropriate approach based on individual needs. For younger patients and athletes, surgical treatment—particularly plate fixation—may be the ideal option. However, conservative treatment remains a viable approach for fractures with minimal displacement.
Meta Description: Midshaft clavicle fractures are a common orthopedic issue. This article explores the controversies between conservative and surgical treatments, comparing plate fixation and intramedullary nailing.
Disclaimer:
This article and all articles on this website are for reference only by medical professionals; specific medical problems should be treated promptly. To ensure “originality” and improve delivery efficiency, some articles on this website are AI-generated and machine-translated, which may be inappropriate or even wrong. Please refer to the original English text or leave a message if necessary. Copyright belongs to the original author. If your rights are violated, please contact the backstage to delete them. If you have any questions, please leave a message through the backstage, or leave a message below this article. Thank you!
Like and share, your hands will be left with the fragrance!