High tibial osteotomy (HTO) is a pivotal surgical procedure for correcting medial compartment knee osteoarthritis and malalignment. However, a critical decision lies in choosing between subtubercle osteotomy (RT-OWHTO) and supratubercle osteotomy (ST-OWHTO). Each technique comes with distinct implications for patellofemoral alignment, surgical complexity, and postoperative outcomes. This article explores the pros and cons of both approaches, helping surgeons make informed decisions during preoperative planning.
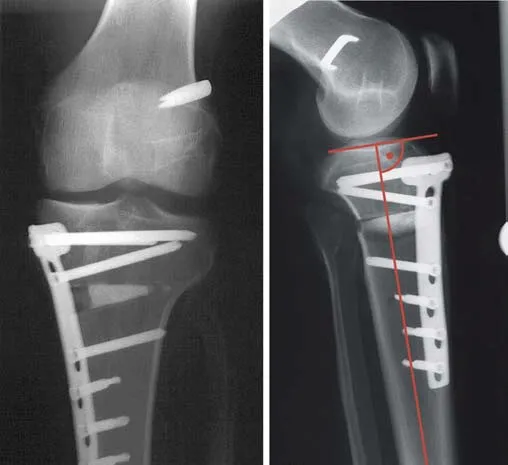
Understanding Subtubercle and Supratubercle Osteotomy
What Sets RT-OWHTO Apart?
Subtubercle osteotomy involves cutting the tibia below the tibial tubercle. This technique is often preferred for maintaining patellofemoral alignment, as it avoids altering the patellar height. However, RT-OWHTO is technically more challenging, with a heightened risk of complications such as tibial tubercle fractures and posterior tibial slope (PTS) increase.
Advantages of ST-OWHTO
In contrast, supratubercle osteotomy involves cutting above the tibial tubercle. While this approach can lower patellar height, as evidenced by reductions in the Blackburne-Peel ratio and Catone-Deschamps index, it simplifies the surgical process and reduces the risk of tubercle-related complications. However, the altered patellofemoral alignment may not translate into significant clinical benefits.
Radiological and Clinical Outcomes
Radiological Insights
Studies, such as those by Cho et al., have revealed that ST-OWHTO leads to a significant decrease in patellar height (average Blackburne-Peel ratio reduction of 13%). Additionally, it increases the TT-TG distance by approximately 3.8mm, potentially affecting patellofemoral tracking. On the other hand, RT-OWHTO preserves patellar height and alignment but comes with a small increase in posterior tibial slope (average increase of 1.69°).
Clinical Implications
Despite these radiological differences, clinical outcomes between the two techniques remain statistically insignificant. While RT-OWHTO may theoretically reduce the risk of long-term patellofemoral osteoarthritis, its technical complexity and risk of complications, including tubercle fractures, make it less appealing in certain scenarios.
Key Considerations for Surgeons
Advantages of RT-OWHTO
- Maintains patellofemoral alignment: Ideal for patients with existing low patellar height.
- Potential long-term benefits: May reduce the risk of patellofemoral osteoarthritis progression.
Challenges with RT-OWHTO
- Technical complexity: Increased risk of tibial tubercle fractures and delayed healing.
- Posterior tibial slope increase: Problematic in cases requiring ACL stabilization.
Advantages of ST-OWHTO
- Simpler procedure: Reduces surgical difficulty and tubercle-related complications.
- Lower patellar height: May facilitate future total knee arthroplasty (TKA) by improving surgical access.
Challenges with ST-OWHTO
- Altered patellofemoral alignment: TT-TG distance and Q-angle changes may impact joint mechanics.
- No clear clinical superiority: Limited evidence of better patient outcomes compared to RT-OWHTO.
Making the Right Choice
When to Choose RT-OWHTO
Surgeons may opt for RT-OWHTO in cases where maintaining patellar height is critical, such as patients with low patella or those at risk of patellofemoral complications. However, meticulous planning is essential to mitigate risks like tubercle fractures.
When to Choose ST-OWHTO
ST-OWHTO is typically preferred for its simplicity and lower complication rates. It is particularly suitable for patients without significant patellofemoral issues or those requiring future TKA.
Conclusion
Selecting between subtubercle and supratubercle osteotomy involves balancing technical complexity, radiological outcomes, and long-term benefits. While RT-OWHTO offers theoretical advantages in preserving patellofemoral alignment, its risks cannot be overlooked. On the other hand, ST-OWHTO simplifies the procedure and may ease future surgical interventions, albeit with changes in patellar mechanics. Ultimately, the choice should be tailored to each patient’s anatomical and clinical needs, ensuring optimal results with minimal complications.