Galeazzi fractures, characterized by a fracture of the radial shaft with disruption of the distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ), are notoriously unstable injuries that demand precise surgical management. Without proper treatment, these fractures can result in chronic instability, pain, and functional impairment. This article provides a comprehensive treatment algorithm that ensures anatomic reduction, DRUJ stability, and optimal recovery.
What is a Galeazzi Fracture?
A Galeazzi fracture involves a fracture of the distal third of the radius combined with an injury to the DRUJ. These injuries are often caused by high-energy trauma, such as falls on an outstretched hand or motor vehicle accidents. The hallmark of this fracture pattern is DRUJ instability, which requires careful intraoperative assessment and tailored treatment.
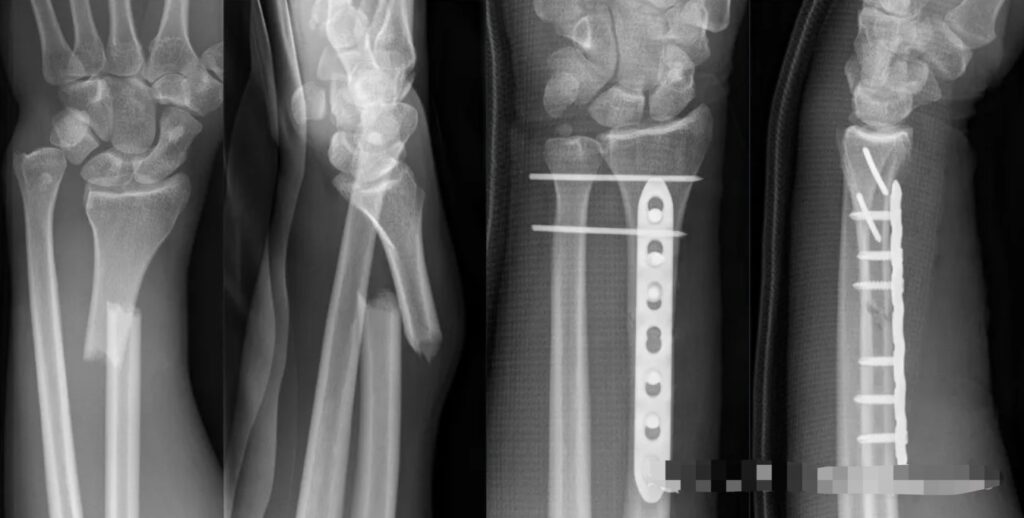
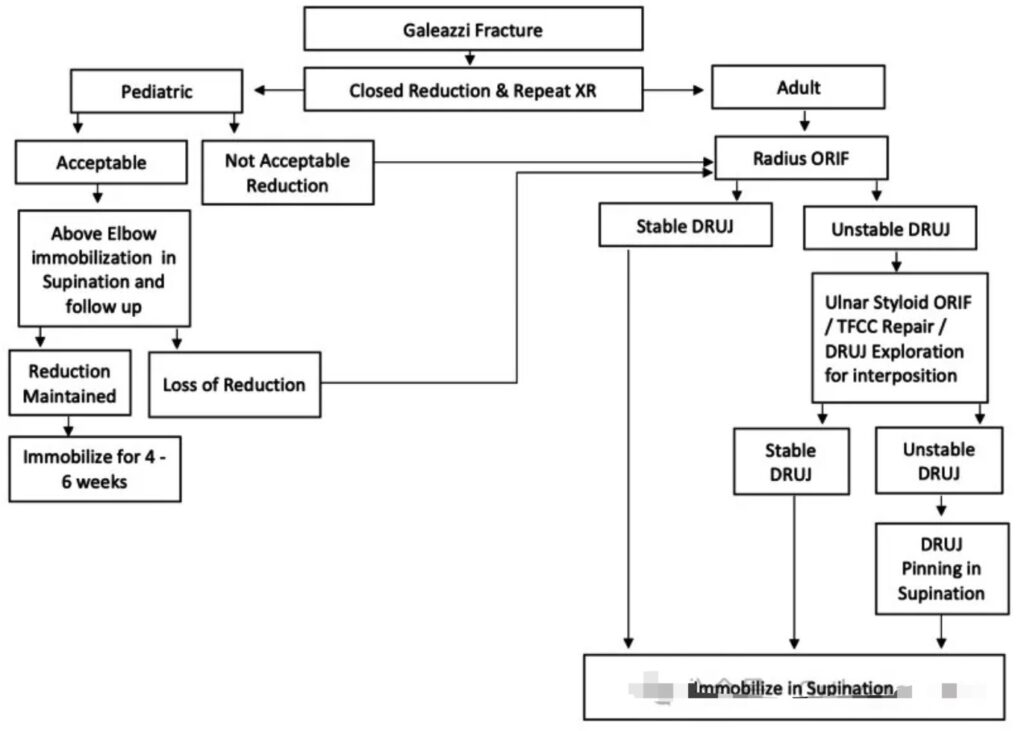
Step-by-Step Treatment Algorithm for Galeazzi Fractures
Step 1: Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF) of the Radial Shaft
The cornerstone of treating Galeazzi fractures is achieving anatomic reduction of the radial shaft. This is accomplished using a low-contact dynamic compression plate (LC-DCP), which provides rigid fixation and restores the natural alignment of the radius.
- Why ORIF? Proper alignment of the radius is critical for restoring the biomechanics of the forearm and ensuring DRUJ stability.
- Key Considerations: Ensure precise reduction on both AP and lateral views to prevent rotational deformities.
Step 2: Intraoperative Assessment of the DRUJ
Once the radial shaft is stabilized, the distal radioulnar joint must be evaluated for reduction and stability. This step is crucial for determining the next course of action.
- Confirm DRUJ reduction on AP and lateral radiographs.
- Assess stability by testing the joint in supination and pronation.
Step 3: Classify the DRUJ
After assessment, classify the DRUJ into one of three categories:
- Reduced and stable
- Reduced and unstable
- Irreducible
This classification guides the subsequent management steps.
Step 4: Management Based on DRUJ Stability
1. Reduced and Stable DRUJ
- If the DRUJ is reduced and stable, no additional surgical intervention is required.
- Management: Apply a protective splint and initiate early motion to prevent stiffness.
2. Reduced and Unstable DRUJ
An unstable DRUJ requires further evaluation to identify the underlying cause of instability, which may involve:
- Large ulnar styloid fractures
- Triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) tears
Management Strategies:
- No ulnar styloid fracture or TFCC tear:
- Stabilize the DRUJ with K-wire fixation between the ulna and radius.
- Ulnar styloid fracture present:
- Perform ORIF of the ulnar styloid using a lag screw, tension band, or K-wire to restore stability.
- TFCC tear identified:
- Repair the tear using suture anchors or drill holes.
- Stabilize the DRUJ with K-wire fixation in supination.
3. Irreducible DRUJ
An irreducible DRUJ suggests the presence of an obstruction, such as:
- Extensor carpi ulnaris (ECU) tendon entrapment
- Fracture fragments
Management Steps:
- Perform surgical exploration to remove the block.
- Reassess the DRUJ for reduction and stability.
- Treat the joint as either stable or unstable based on findings.
Key Points in Galeazzi Fracture Management
Why DRUJ Stability Matters
The DRUJ plays a vital role in forearm rotation and load transmission. Failure to address DRUJ instability can lead to:
- Chronic pain
- Arthritis
- Loss of forearm rotation
Common Complications
Despite meticulous surgical management, Galeazzi fractures may result in complications such as:
- Nonunion of the radial shaft
- Persistent DRUJ instability
- Ulnar nerve irritation
- Joint stiffness
Conclusion
The treatment of Galeazzi fractures demands a systematic algorithm to address both the radial shaft fracture and the distal radioulnar joint. By following this step-by-step approach—starting with radial ORIF, assessing the DRUJ, and managing instability appropriately—surgeons can achieve optimal outcomes and restore forearm function.
For more information on Galeazzi fractures, visit the Orthopaedic Trauma Association.
SEO Keywords and Tags
Primary Keywords
- Galeazzi fractures
- DRUJ instability
- Radial shaft ORIF
Secondary Keywords
- Galeazzi fracture treatment algorithm
- Distal radioulnar joint injuries
- TFCC tear management
Long-Tail Keywords
- How to treat Galeazzi fractures with unstable DRUJ
- Surgical steps for Galeazzi fracture fixation
- ORIF with LC-DCP for radial shaft fractures
Disclaimer:
This article and all articles on this website are for reference only by medical professionals; specific medical problems should be treated promptly. To ensure “originality” and improve delivery efficiency, some articles on this website are AI-generated and machine-translated, which may be inappropriate or even wrong. Please refer to the original English text or leave a message if necessary. Copyright belongs to the original author. If your rights are violated, please contact the backstage to delete them. If you have any questions, please leave a message through the backstage, or leave a message below this article. Thank you!
Like and share, your hands will be left with the fragrance!