Orthopedic trauma surgery is a constantly evolving field, where precision, innovation, and a deep understanding of biomechanics and biology are essential for success. From helical plates to minimally invasive osteosynthesis (MIO), this article delves into cutting-edge techniques, challenges, and solutions for fracture fixation. Whether you’re addressing implant fatigue, trochanteric fractures, or surgical invasiveness, these insights will help refine your approach and improve patient outcomes.
Helical Plates: Revolutionizing Fracture Fixation
What Are Helical Plates?
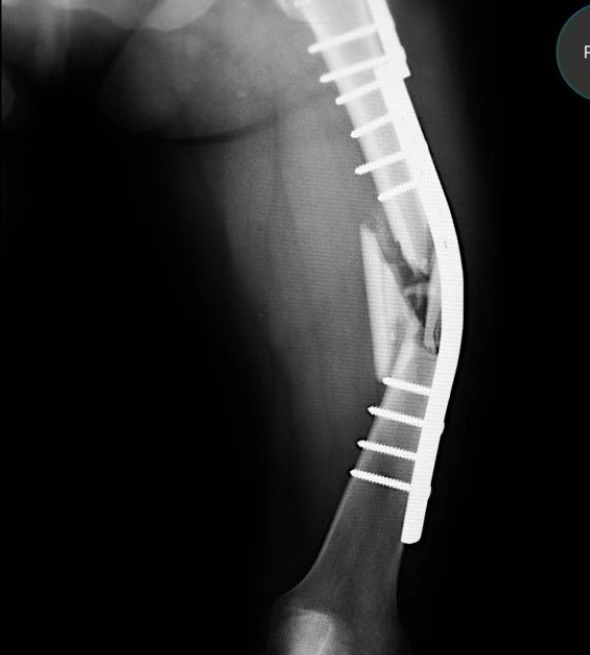
The helical plate is a game-changer in fracture treatment, particularly for bridging defects and preventing implant fatigue failure. Unlike traditional plates, it is a slightly twisted or bent straight plate, offering enhanced stiffness and strength while preserving the bone’s blood supply.
- Minimally invasive design: The helical shape allows insertion through a small incision distally, maintaining the original proximal surgical approach.
- Biological preservation: As a part of MIPO (Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis), it minimizes damage to blood supply and avoids “contact osteoporosis.”
- Increased stability: It protects initial plate fixation by reducing bending loads, particularly in cases of segmental comminution where bone support is lacking.
Clinical Advantages
The helical plate has proven effective in various long bone fractures, offering solutions where conventional plates fail. For example:
- In multi-fragmentary fractures, where traditional plates may suffer from fatigue or screw breakage, the helical plate provides efficient unloading with minimal trauma.
- It enables early pain-free weight bearing, even in cases with low strain conditions that might otherwise delay healing.
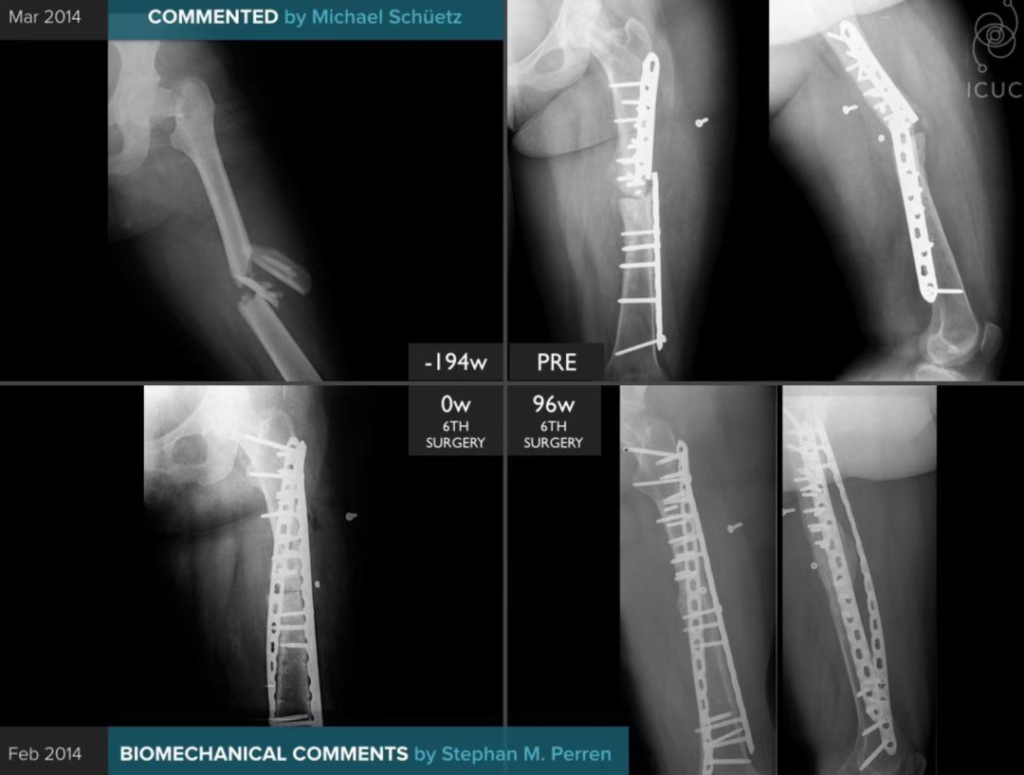
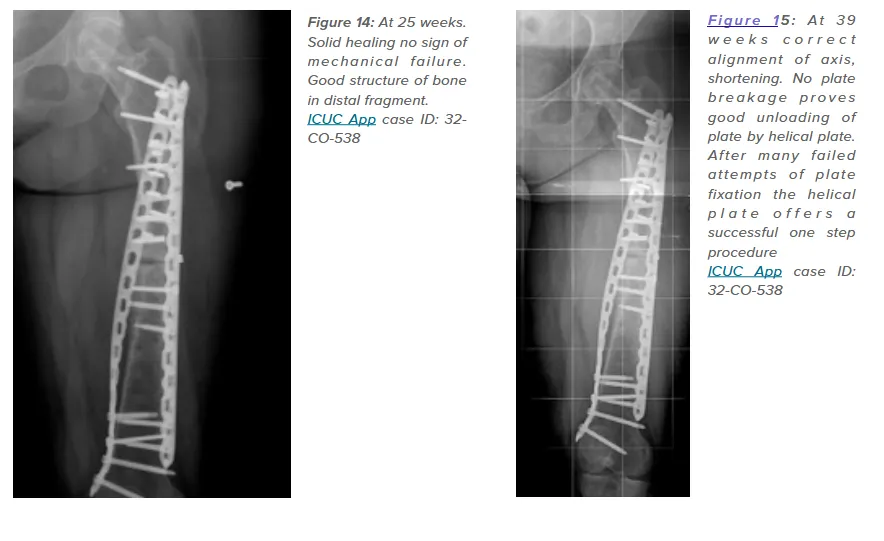
One notable case (ICUC App ID: 32-CO-538) involved a young patient with repeated plate failures for a comminuted femoral shaft fracture. The addition of a helical plate reduced bending loads, resulting in solid healing and no mechanical failure at 25 weeks. This underscores the potential of helical plates to prevent fatigue failures and support early functional recovery.
Balancing Stability and Biology in Fracture Fixation
Biomechanical Considerations
Achieving the right balance between mechanical stability and biological preservation is critical in orthopedic trauma surgery. Missteps in this balance can lead to complications such as implant failure, delayed healing, or non-union.
- Stability vs. strain: Excessive stiffness (low strain) hinders callus formation, while excessive movement (high strain) prevents solid bridging.
- Blood supply: Techniques like periosteal stripping or poorly designed implants can impair blood flow, delaying fracture healing. Elevated plates reduce contact with the bone, preserving vascular integrity.
Innovative Solutions
- Helical plates: These plates address the challenge of maintaining both strength and biology, providing stability without compromising blood supply.
- MIO techniques: Minimally invasive approaches reduce tissue trauma, promoting faster recovery and reducing infection risks.
Minimally Invasive Osteosynthesis (MIO): Reducing Surgical Trauma

Why MIO Matters
Surgical invasiveness directly impacts patient outcomes. Excessive tissue trauma can impair fracture healing, reduce infection resistance, and increase recovery times. MIO aims to minimize these risks by leaving “small surgical footprints.”
- Soft tissue preservation: Careful handling of soft tissues and avoiding excessive traction are essential.
- Precise reduction: MIO focuses on achieving anatomic reduction and stable fixation, particularly in articular fractures and complex shaft fractures.
- Balancing risks: While MIO reduces surgical trauma, it may increase the risk of nerve or vessel injury. Surgeons must weigh these factors carefully.
Clinical Applications
MIO is particularly effective in cases where biological preservation is critical. For example:
- Trochanteric fractures: Using MIO cerclage wires improves reduction while minimizing vascular damage.
- Helical plates: These can be inserted with minimal additional incisions, reducing trauma and preserving blood supply.
Addressing Specific Fracture Challenges
Trochanteric Fractures
Trochanteric fractures are among the most common and costly to treat. Understanding the fracture pattern is more important than implant choice. Key considerations include:
- Avoiding cut-outs: Proper placement of implants in the femoral head is essential. Avoid the superior and anterior hemispheres.
- Rotational instability: Anti-rotation devices, such as trochanteric buttress plates, are critical.
- Reduction quality: Poor reduction can lead to complications like varus displacement or fragmentation of the lateral cortex.
Dorsal Ulnar Corner Fractures
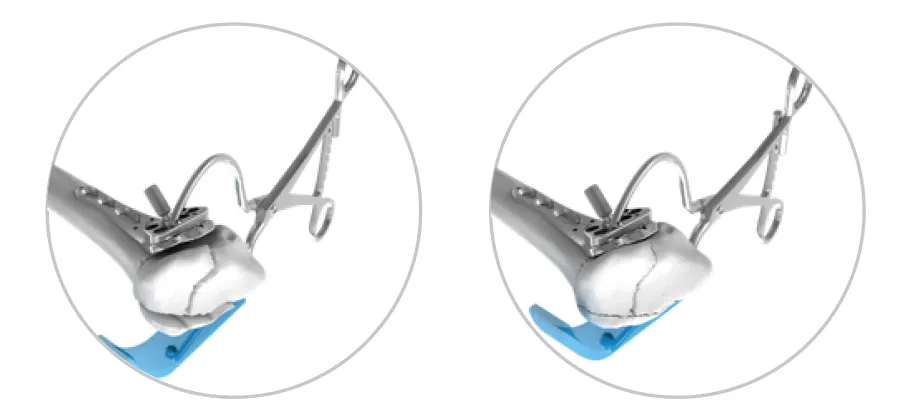
These fractures uniquely affect both the radiolunate and distal radioulnar joints. A single volar approach using a ball-tipped reduction clamp has shown excellent results, achieving anatomic reduction with minimal tissue stripping.
Ankle Fractures
For pilon fractures and complex malleolar fractures, classifications alone are insufficient. Adding a detailed “problems inventory” (e.g., comminution zones, articular impaction) to the treatment plan ensures better outcomes.
Evaluating Surgical Performance and Learning
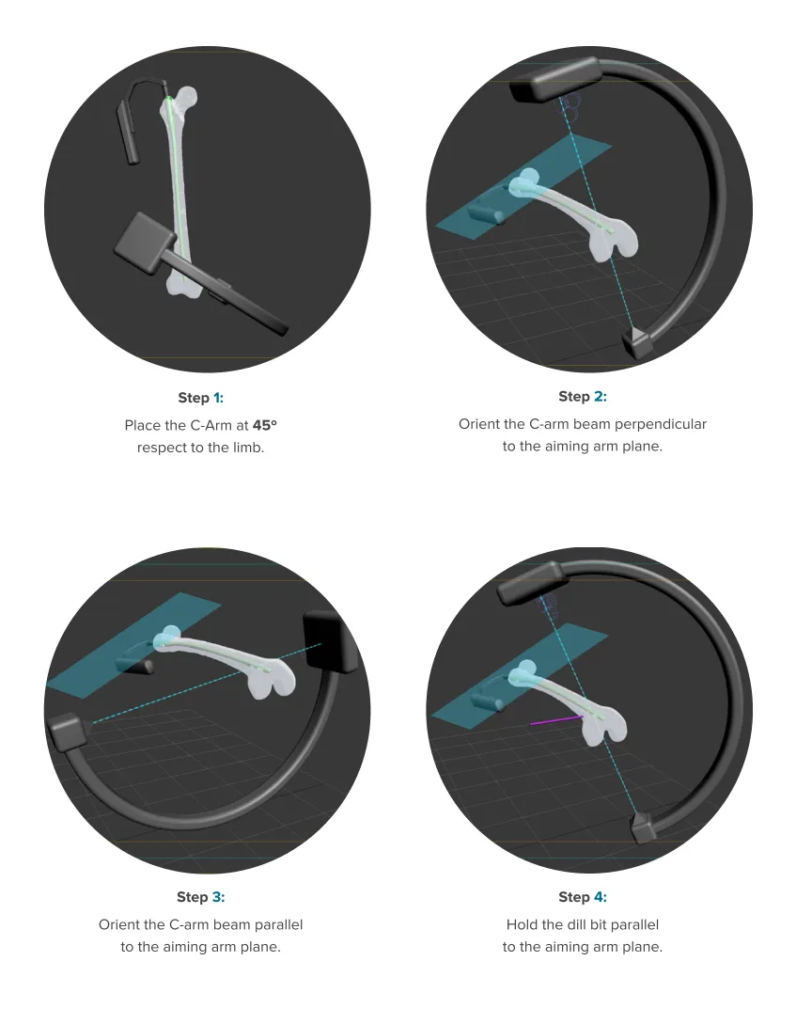
The Importance of Documentation
Analyzing surgical outcomes is crucial for improvement. Tools like the ICUC App provide detailed documentation, allowing surgeons to compare work-as-planned with work-as-done. This retrospective analysis helps identify technical errors and refine surgical techniques.
Learning from Complications
Complications often provide valuable insights into biomechanical phenomena. For example:
- Lag screw failures: Highlight the importance of balancing implant stiffness and strength.
- Screw stripping: Techniques like milling the screw head for removal can prevent further complications.
Disclaimer:
This article and all articles on this website are for reference only by medical professionals; specific medical problems should be treated promptly. To ensure “originality” and improve delivery efficiency, some articles on this website are AI-generated and machine-translated, which may be inappropriate or even wrong. Please refer to the original English text or leave a message if necessary. Copyright belongs to the original author. If your rights are violated, please contact the backstage to delete them. If you have any questions, please leave a message through the backstage, or leave a message below this article. Thank you!
Like and share, your hands will be left with the fragrance!