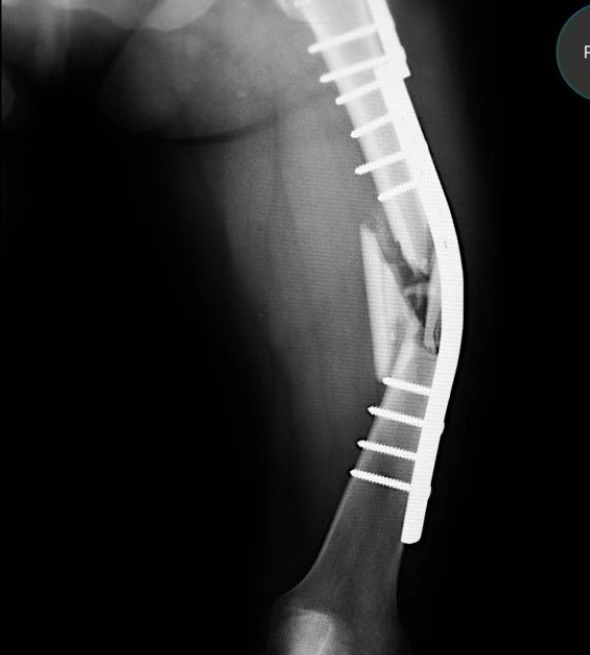
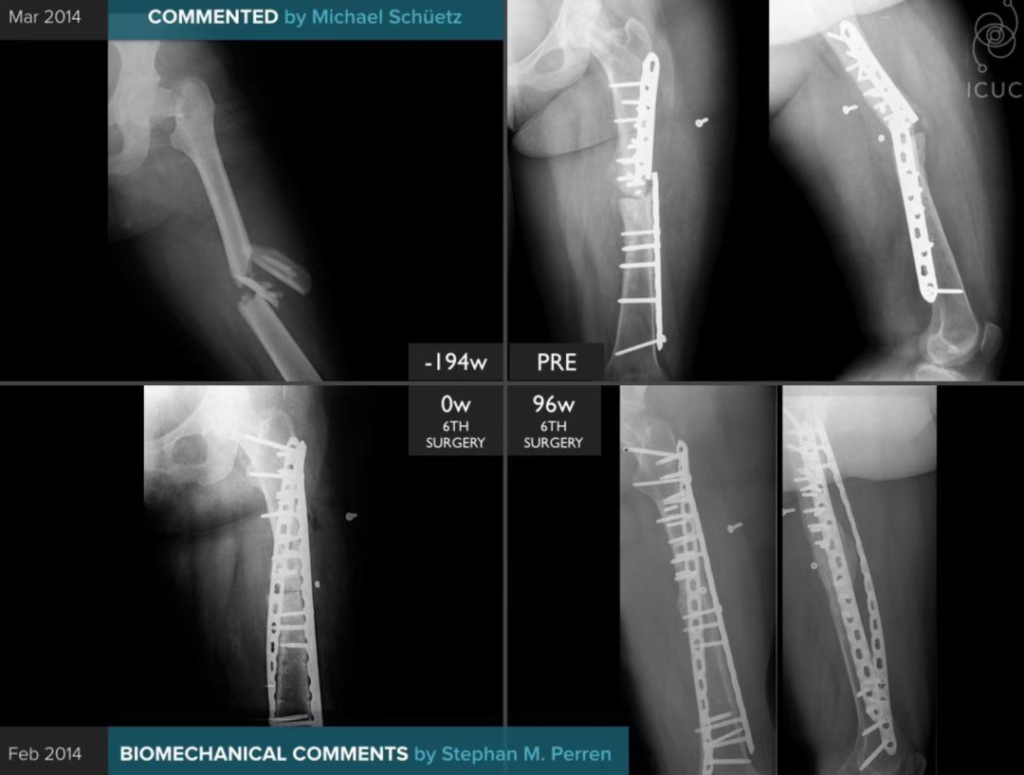
Distal humeral fractures represent a unique challenge in orthopedic trauma surgery. While less common than fractures of the humeral shaft or proximal humerus, their complex anatomy, variable fracture patterns, and propensity for complications demand a tailored approach. The debate between intramedullary nailing (IMN) and plate fixation (ORIF) continues to evolve, with both methods offering distinct advantages and drawbacks. This article explores the biomechanical considerations, surgical techniques, and potential complications associated with these two approaches, providing insights for surgeons navigating this difficult fracture type.
Understanding Distal Humeral Fractures
Prevalence and Mechanisms
Distal humeral fractures occur across a wide age spectrum, with younger patients typically sustaining high-energy trauma and older individuals experiencing low-energy injuries due to osteoporosis. These fractures often involve the articular surfaces of the elbow joint, making stable fixation essential to prevent joint stiffness—a debilitating complication that can severely limit elbow function.
Treatment Goals
The primary objectives in managing distal humeral fractures are:
- Restoring elbow joint congruity for optimal function.
- Achieving stable fixation to enable early postoperative mobilization.
- Minimizing the risk of complications, such as nonunion, malunion, and nerve injuries.
Intramedullary Nailing (IMN): A Load-Sharing Solution
Biomechanical Advantages
Intramedullary nails are recognized for their load-sharing properties, which reduce stress shielding at the fracture site. This biomechanical feature promotes bone healing by allowing controlled load transfer to the bone. In the context of distal humeral fractures, retrograde nailing is favored over antegrade techniques to avoid rotator cuff complications.
Key benefits of IMN include:
- Preservation of soft tissues: IMN is less invasive compared to plate fixation, minimizing surgical trauma.
- Enhanced bending and torsional stiffness: Retrograde nailing provides superior initial stability for distal fractures compared to antegrade approaches.
- Reduced refracture risk: The load-sharing nature decreases the likelihood of refracture after implant removal.
Challenges
Despite these advantages, IMN faces technical hurdles in distal humeral fractures:
- Distal locking difficulties: Achieving rotational stability in the distal humerus is challenging due to its narrow canal and proximity to neurovascular structures.
- Limited working distance: The intricate anatomy of the distal humerus complicates nail placement and screw fixation.
- Intra-articular fractures: IMN may not provide sufficient stability for fractures involving the elbow joint surface, requiring precise reduction techniques.
Plate Fixation (ORIF): Angular Stability and Anatomical Reduction
Biomechanical Strength
Plate fixation, particularly using precontoured anatomical locking plates, is widely regarded as the gold standard for distal humeral fractures. Dual-plate fixation, involving plates on the medial and lateral columns, ensures optimal stability by addressing the triangle of stability—a critical concept in elbow biomechanics.
Key features of plate fixation include:
- Direct visualization: ORIF allows surgeons to achieve anatomical reduction, crucial for restoring joint congruity in intra-articular fractures.
- Angular stability: Locking plates create a fixed-angle construct, providing superior fixation in osteoporotic bone.
- Early mobilization: The rigid stability of plates facilitates immediate postoperative movement, reducing the risk of elbow stiffness.
Challenges
Plate fixation is not without its limitations:
- Extensive soft tissue dissection: ORIF requires a larger surgical exposure, increasing the risk of nerve injuries, particularly to the ulnar nerve.
- Hardware complications: Screw loosening, plate breakage, and joint penetration are common issues, especially in elderly patients with poor bone quality.
- Complex fracture patterns: Securing small, comminuted distal fragments can be technically demanding.
Comparing IMN and Plate Fixation: Mechanics, Working Distance, and Complications
Biomechanical Considerations
When comparing IMN and plate fixation, several factors emerge:
- Load-sharing vs angular stability: IMN offers better load-sharing, while plates provide angular stability essential for intra-articular fractures.
- Soft tissue impact: IMN is less invasive, but plates allow for direct visualization and anatomical reduction.
- Risk of stress shielding: Plates may increase stress shielding, potentially leading to refracture after implant removal.
Surgical Technique
- IMN: Retrograde nailing requires precise entry point placement near the olecranon fossa and meticulous distal locking to avoid iatrogenic fractures or neurovascular injury.
- Plate fixation: ORIF often involves dual plating with either parallel or orthogonal configurations, tailored to the fracture pattern. Techniques like olecranon osteotomy may be employed for better exposure.
Complications
Both methods are associated with distinct risks:
- IMN complications:
- Iatrogenic fractures during nail insertion.
- Rotational instability due to inadequate distal locking.
- Shoulder impingement (antegrade nailing).
- Plate fixation complications:
- Ulnar nerve injury due to surgical exposure.
- Hardware failure (screw loosening, plate breakage).
- Heterotopic ossification around the elbow joint.
Hybrid Approaches: Combining IMN and Plates
For segmental fractures involving both the humeral shaft and distal articular region, combined nail-plate constructs are emerging as a promising solution. This approach leverages the load-sharing properties of IMN for shaft stabilization and the angular stability of plates for distal fixation. Early studies suggest this hybrid method may reduce complications and improve outcomes in complex fractures.
Recent Advances and Future Directions
Innovations in Implant Design
- Precontoured plates: Anatomically shaped plates designed for the distal humerus improve fit and reduce surgical time.
- Internal distal locking nails: Advanced nail designs eliminate the need for distal locking screws, minimizing neurovascular risks.
Technological Tools
- 3D-printed fracture models: Patient-specific models enhance preoperative planning and surgical accuracy.
- Biomechanical modeling: Advanced imaging techniques allow personalized fixation strategies based on fracture characteristics.
Research Opportunities
Future studies should focus on:
- Comparative outcomes between IMN and plate fixation for distal humeral fractures.
- Long-term performance of hybrid nail-plate constructs.
- Optimal plating configurations (parallel vs orthogonal) for specific fracture patterns.
Conclusion
The management of distal humeral fractures requires a nuanced approach, balancing biomechanical stability, surgical feasibility, and complication risks. Both intramedullary nailing and plate fixation offer valuable solutions, but neither is universally optimal. Surgeons must consider the fracture pattern, patient factors, and technical demands to select the most appropriate method. As hybrid techniques and implant designs continue to evolve, the future of distal humeral fracture treatment promises improved outcomes and fewer complications.
Meta Description
Explore the biomechanics, surgical techniques, and complications of intramedullary nailing vs plate fixation for distal humeral fractures. Learn how hybrid approaches and advanced implant designs are shaping the future of orthopedic trauma surgery.
Keywords
- Distal humeral fractures
- Intramedullary nailing vs plate fixation
- Orthopedic trauma surgery
- Retrograde nailing for distal humerus
- Plate fixation for elbow fractures
- Complications of distal humeral fracture fixation
- Comparing IMN and ORIF for distal humerus fractures
- Best surgical techniques for distal humeral fractures
- Hybrid nail-plate constructs for complex humeral fractures
#OrthopedicTrauma #DistalHumerusFractures #IntramedullaryNailing #PlateFixation #ElbowSurgery
Disclaimer:
This article and all articles on this website are for reference only by medical professionals; specific medical problems should be treated promptly. To ensure “originality” and improve delivery efficiency, some articles on this website are AI-generated and machine-translated, which may be inappropriate or even wrong. Please refer to the original English text or leave a message if necessary. Copyright belongs to the original author. If your rights are violated, please contact the backstage to delete them. If you have any questions, please leave a message through the backstage, or leave a message below this article. Thank you!
Like and share, your hands will be left with the fragrance!